Diesel Service Technicians and Mechanics
Average Salary (US)
$48,690
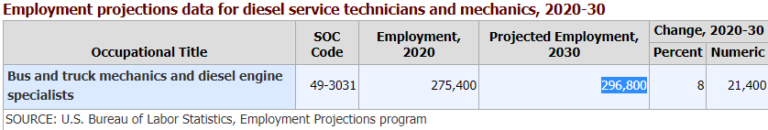
PROJECTED JOB OUTLOOK 2020-30
8%
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Diesel Service Technicians and Mechanics, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/installation-maintenance-and-repair/diesel-service-technicians-and-mechanics.htm